In
the previous section we completed the checks and 'rules' for distributing the bars in a beam. Now we will discuss about the check for deflection control. When loads act on the beam, it deflects. If this deflection is excessive, following undesirable effects may be produced:
• Appearance and efficiency of the structure is affected
• Appearance and efficiency of the partitions and equipments that the structure supports is affected
• Psychological discomfort is caused to the occupants
• Slopes and levels of the floor surfaces are affected
• Wider cracks are formed on the under side of beams and slabs, which will affect their durability
• Deflection of a roof slab will lead to ponding of water over the roof
So we must make sure that the deflection is kept within specified limits. Let us see how this can be done:
The total depth D of a beam or a slab has a major role to play in controlling deflection. We can prove this by taking the example of a beam made completely with a linear elastic material like steel. We will later extend our discussion to reinforced concrete which is a composite material.
Consider one such beam. Let it be simply supported and carry a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length. It has a length of l. We know that the deflection Δ at midspan of such a beam is given by
Eq.4.12
Where l = length of the beam
E = Young's modulus of elasticity of the material of the beam
w = Load per unit length of the beam, and
I = Moment of inertia of the beam section = bd3 /12
We also know that the maximum bending moment Mmax occurs at the midspan, and is given by
Eq.4.13
Mmax = wl2/8
From the above Eq.4.13, we get
Eq.4.14
w = 8Mmax / l2
Now we take the basic bending equation:
M/I = f/y = E/R . Here we need only the first two ratios. We get:
Eq.4.15
M = (f/y)I
Let us apply Eq.4.15 to the midspan section of the beam:
M =Mmax; f = Maximum tensile stress at extreme fibre; y = half the total depth of the beam = D/2; I = bd3 /12
So we get
Eq.4.16
Substituting this value of Mmax in 4.14, we get
Eq.4.17
Substituting this value of w in the basic equation for deflection (Eq.4.12), we get
This can be simplified as
Eq.4.18
[240 /1152][ f/E] is taken as a constant because both f and E are constants.
So we get a relation between Δ and D. Δ is in the numerator on the left side and D is the denominator on the right side. So, if we increase D, Δ will decrease. The length l cannot change because it depends on the size and shape of the rooms, or the distance between supporting columns.
We derived the above Eq.4.18 for a simply supported beam, carrying a uniformly distributed load. The expression for Δ (Eq.4.12), and the expression for Mmax (Eq.4.13) are for simply supported beams. We can do similar derivation for other types like continuous beams, fixed beams etc., and also other types of loads such as point loads, uniformly varying loads etc.,. In all those cases, we will get the same equation as in 4.18. The only differences will be in the value of the 'constant'. This means that in all cases, when D increases, Δ decreases.
The Eq.4.18 cannot be applied directly to reinforced concrete because it is not a linearly elastic material. And also the values of f, I and E are dependent on the extend of cracking, percentage of reinforcement and on the long term effects like creep and shrinkage. So how do we apply it to reinforced concrete beams? The answer is that we follow the procedure given in the code. The code adopts the concept that we discussed above for a linearly elastic material, makes some suitable approximations, and prescribes some limiting l/d ratios. So the next topic that we have to discuss is:
Cl.23.2.1 of the code gives us some limiting l/d (span/Effective depth) ratios. Note that here d is the effective depth, not the total depth D. These ratios, which are given by the code are the 'limiting ratios'. We have to calculate our own ratio (denoted as (l/d)actual) with the actual length and effective depth of the beam that we are designing, and compare it with that given by the code. The ratio that we calculate should not be greater than the ratio that is given by the code. Supposing that the value we obtain from the code for a particular problem is '22'. Then the condition can be represented as (l/d)actual ≤ 22. d is in the denominator. So we can say that when the total depth D increases (then the effective depth d will also increase), we have a better chance for satisfying the condition.
So our next aim is to obtain the value of l/d given by the code. It is not very easy to obtain it from the code. What the code gives us is the (l/d)basic . We have to apply some 'modification factors' to it, to finally obtain the l/d ratio. The 'modification factors' depend upon the particular problem that we are considering. We will now see the values of (l/d)basic and the modification factors:
Code recommendations for (l/d)basic:
For reinforced concrete beams of rectangular cross section and slabs of uniform thickness, cl 23.2.1(a) gives the following values:
4.19:
(l/d)basic for spans upto 10m:
Cantilever 7
Simply supported 20
Continuous 26
Modification factor α
According to section (b) of the above clause, when the span is greater than 10m, for simply supported and continuous members, we must find the ratio 'α = span/10' and multiply it to the above basic values.
But for cantilevers, when the span is greater than 10m, actual deflection calculations should be made.
Modification factor for tension steel kt
According to section (c) of the above clause, we must calculate a modification factor kt from fig.4. of the code. This modification factor depends upon the area of the tension reinforcement and also the stress in the tension reinforcement. So the first step is to find fst, the stress in the tension steel. In Limit state method, the stresses at ultimate state are considered. So we take the stress when the ultimate load (factored load) is applied on the beam. A newly designed beam will be under reinforced, and so the stress in steel will be 0.87fy. But for deflection control checks, we consider the working loads. So fst is the stress in steel when the working loads are applied on the beam. When we discussed 'Working stress method', we learned how to determine the stresses when any given load is applied on the beam. We can determine it whether the beam is under reinforced or over reinforced. But it involves lengthy calculations. So the code gives us a formula to calculate fst. It is given along with the fig.4 of the code:
The second step is to find the percentage of tension reinforcement. It is given by:
Where Ast,p is the actual area of steel provided
Now we can find the modification factor kt from fig.4 of the code. A presentation demonstrating the general procedure for obtaining required values from graphs is given here.
Modification factor kc
According to section (d) of the above clause, we must calculate a 'modification factor' kc from fig.5. of the code. This modification factor depends upon the area of the compression reinforcement. So we will discuss about it when we take up the design of doubly reinforced sections. This factor need not be calculated when we design singly reinforced sections.
Modification factor kf
According to section (e) of the above clause, we must calculate a 'reduction factor' kf from fig.6. This reduction factor is for flanged sections. So we will discuss about it when we take up the design of flanged sections. This factor need not be calculated when we design singly reinforced sections.
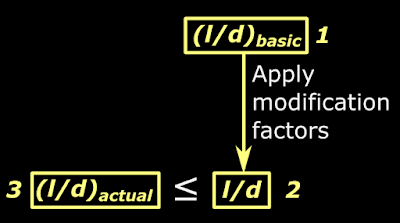
In the above discussion we saw three l/d ratios. They are:
• (l/d)basic which is the basic value given by the code. (4.19 given above)
• l/d which is obtained by applying the required modification factors to (l/d)basic .
• (l/d)actual which is obtained using the finalized values of l and d of the beam which we are designing.
Their application in three steps can be shown in the form of a flowchart as in the fig.4.15 below:
Fig.4.15
Application of l/d ratios
So the above discussions can be summarized as follows:
4.19
For singly reinforced rectangular beams with span less than 10m,
(l/d)actual ≤ [(l/d)basic] kt
4.20
For singly reinforced rectangular beams with span greater than 10m,
(l/d)actual ≤ [(l/d)basic] α kt
If the beam is a cantilever with span greater than 10 m, actual deflection calculations should be made.
Cl.23.2 (a) of the code specifies that the final deflection due to all loads including the effects of temperature, creep and shrinkage and measured from the as-cast level of the ,supports of floors, roofs and all other horizontal members, should not normally exceed span/250.
The method of using 'limiting l/d ratios' that we discussed above is expected to satisfy this requirement.
It should be noted that in cases where the span is large, or loading is heavy, or creep and shrinkage effects are more, or when strict deflection control is required, we must calculate the actual deflection, the method of which is discussed in a later chapter.
So we have completed all the checks that have to be done after the design process. We will now see some solved examples which demonstrate the design procedure and various checks:
Solved example 4.1
Solved example 4.2
Solved example 4.3
So we have completed the design and detailing (for flexure) of simply supported beams. Next we will see the analysis of simply supported one way slabs.
• Appearance and efficiency of the structure is affected
• Appearance and efficiency of the partitions and equipments that the structure supports is affected
• Psychological discomfort is caused to the occupants
• Slopes and levels of the floor surfaces are affected
• Wider cracks are formed on the under side of beams and slabs, which will affect their durability
• Deflection of a roof slab will lead to ponding of water over the roof
So we must make sure that the deflection is kept within specified limits. Let us see how this can be done:
The total depth D of a beam or a slab has a major role to play in controlling deflection. We can prove this by taking the example of a beam made completely with a linear elastic material like steel. We will later extend our discussion to reinforced concrete which is a composite material.
Consider one such beam. Let it be simply supported and carry a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length. It has a length of l. We know that the deflection Δ at midspan of such a beam is given by
Eq.4.12
Where l = length of the beam
E = Young's modulus of elasticity of the material of the beam
w = Load per unit length of the beam, and
I = Moment of inertia of the beam section = bd3 /12
We also know that the maximum bending moment Mmax occurs at the midspan, and is given by
Eq.4.13
Mmax = wl2/8
From the above Eq.4.13, we get
Eq.4.14
w = 8Mmax / l2
Now we take the basic bending equation:
M/I = f/y = E/R . Here we need only the first two ratios. We get:
Eq.4.15
M = (f/y)I
Let us apply Eq.4.15 to the midspan section of the beam:
M =Mmax; f = Maximum tensile stress at extreme fibre; y = half the total depth of the beam = D/2; I = bd3 /12
So we get
Eq.4.16
Substituting this value of Mmax in 4.14, we get
Eq.4.17
Substituting this value of w in the basic equation for deflection (Eq.4.12), we get
This can be simplified as
Eq.4.18
[240 /1152][ f/E] is taken as a constant because both f and E are constants.
So we get a relation between Δ and D. Δ is in the numerator on the left side and D is the denominator on the right side. So, if we increase D, Δ will decrease. The length l cannot change because it depends on the size and shape of the rooms, or the distance between supporting columns.
We derived the above Eq.4.18 for a simply supported beam, carrying a uniformly distributed load. The expression for Δ (Eq.4.12), and the expression for Mmax (Eq.4.13) are for simply supported beams. We can do similar derivation for other types like continuous beams, fixed beams etc., and also other types of loads such as point loads, uniformly varying loads etc.,. In all those cases, we will get the same equation as in 4.18. The only differences will be in the value of the 'constant'. This means that in all cases, when D increases, Δ decreases.
The Eq.4.18 cannot be applied directly to reinforced concrete because it is not a linearly elastic material. And also the values of f, I and E are dependent on the extend of cracking, percentage of reinforcement and on the long term effects like creep and shrinkage. So how do we apply it to reinforced concrete beams? The answer is that we follow the procedure given in the code. The code adopts the concept that we discussed above for a linearly elastic material, makes some suitable approximations, and prescribes some limiting l/d ratios. So the next topic that we have to discuss is:
Code procedure for deflection control
Cl.23.2.1 of the code gives us some limiting l/d (span/Effective depth) ratios. Note that here d is the effective depth, not the total depth D. These ratios, which are given by the code are the 'limiting ratios'. We have to calculate our own ratio (denoted as (l/d)actual) with the actual length and effective depth of the beam that we are designing, and compare it with that given by the code. The ratio that we calculate should not be greater than the ratio that is given by the code. Supposing that the value we obtain from the code for a particular problem is '22'. Then the condition can be represented as (l/d)actual ≤ 22. d is in the denominator. So we can say that when the total depth D increases (then the effective depth d will also increase), we have a better chance for satisfying the condition.
So our next aim is to obtain the value of l/d given by the code. It is not very easy to obtain it from the code. What the code gives us is the (l/d)basic . We have to apply some 'modification factors' to it, to finally obtain the l/d ratio. The 'modification factors' depend upon the particular problem that we are considering. We will now see the values of (l/d)basic and the modification factors:
Code recommendations for (l/d)basic:
For reinforced concrete beams of rectangular cross section and slabs of uniform thickness, cl 23.2.1(a) gives the following values:
4.19:
(l/d)basic for spans upto 10m:
Cantilever 7
Simply supported 20
Continuous 26
Modification factor α
According to section (b) of the above clause, when the span is greater than 10m, for simply supported and continuous members, we must find the ratio 'α = span/10' and multiply it to the above basic values.
But for cantilevers, when the span is greater than 10m, actual deflection calculations should be made.
Modification factor for tension steel kt
According to section (c) of the above clause, we must calculate a modification factor kt from fig.4. of the code. This modification factor depends upon the area of the tension reinforcement and also the stress in the tension reinforcement. So the first step is to find fst, the stress in the tension steel. In Limit state method, the stresses at ultimate state are considered. So we take the stress when the ultimate load (factored load) is applied on the beam. A newly designed beam will be under reinforced, and so the stress in steel will be 0.87fy. But for deflection control checks, we consider the working loads. So fst is the stress in steel when the working loads are applied on the beam. When we discussed 'Working stress method', we learned how to determine the stresses when any given load is applied on the beam. We can determine it whether the beam is under reinforced or over reinforced. But it involves lengthy calculations. So the code gives us a formula to calculate fst. It is given along with the fig.4 of the code:
The second step is to find the percentage of tension reinforcement. It is given by:
Where Ast,p is the actual area of steel provided
Now we can find the modification factor kt from fig.4 of the code. A presentation demonstrating the general procedure for obtaining required values from graphs is given here.
Modification factor kc
According to section (d) of the above clause, we must calculate a 'modification factor' kc from fig.5. of the code. This modification factor depends upon the area of the compression reinforcement. So we will discuss about it when we take up the design of doubly reinforced sections. This factor need not be calculated when we design singly reinforced sections.
Modification factor kf
According to section (e) of the above clause, we must calculate a 'reduction factor' kf from fig.6. This reduction factor is for flanged sections. So we will discuss about it when we take up the design of flanged sections. This factor need not be calculated when we design singly reinforced sections.
In the above discussion we saw three l/d ratios. They are:
• (l/d)basic which is the basic value given by the code. (4.19 given above)
• l/d which is obtained by applying the required modification factors to (l/d)basic .
• (l/d)actual which is obtained using the finalized values of l and d of the beam which we are designing.
Their application in three steps can be shown in the form of a flowchart as in the fig.4.15 below:
Fig.4.15
Application of l/d ratios
So the above discussions can be summarized as follows:
4.19
For singly reinforced rectangular beams with span less than 10m,
(l/d)actual ≤ [(l/d)basic] kt
4.20
For singly reinforced rectangular beams with span greater than 10m,
(l/d)actual ≤ [(l/d)basic] α kt
If the beam is a cantilever with span greater than 10 m, actual deflection calculations should be made.
Cl.23.2 (a) of the code specifies that the final deflection due to all loads including the effects of temperature, creep and shrinkage and measured from the as-cast level of the ,supports of floors, roofs and all other horizontal members, should not normally exceed span/250.
The method of using 'limiting l/d ratios' that we discussed above is expected to satisfy this requirement.
It should be noted that in cases where the span is large, or loading is heavy, or creep and shrinkage effects are more, or when strict deflection control is required, we must calculate the actual deflection, the method of which is discussed in a later chapter.
So we have completed all the checks that have to be done after the design process. We will now see some solved examples which demonstrate the design procedure and various checks:
Solved example 4.1
Solved example 4.2
Solved example 4.3
So we have completed the design and detailing (for flexure) of simply supported beams. Next we will see the analysis of simply supported one way slabs.